Downlink NOMA System with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Application of custom REINFORCE algorithm to downlink NOMA system
This research is published in The Journal of Korean Institute of Communication and Information Scienes (JKICS) in March 2025. If you’re interested, please check out the paper.
Brief Introduction to The Project
As the growth of the expansion of the internet of things (IoT), the issue with a scarcity of network resources arised. In order for wireless network (communication) to be successfully accomplished and fully utilized, optimizing the use of the resources is a key to it. There are numerous aspects to consider when managing networking resources, such as user fairness, quality of service (QoS), and throughput efficiency.
In recent years, the Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) system has been considered as a promising candidate for a multiple access framework due to its performance allowing multiple users to access to channels at the same time. The NOMA system involves two fundamental problems: channel assignment and power allocation. While the NOMA system is considered to be a promising technique for communication, it has a few limitations as the resource allocation problem, which involves channel assignment and power allocation, is considered to be NP-hard.
In this project, in order to overcome the NP-hardness of the problem, Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) is used when finding an optimal channel assignment. By applying DRL techniques to the project, the agent successfully managed finite and scarce networking resources efficiently, achieving near-optimal throughput.
Background
In this page, background knowledge of wireless networking systems will not be covered. Instead, please refer to the following page:
System Model
In this project, we assume downlink NOMA system where the base station (BS) sends data to multiple users in a wireless channels. As the eseential of the project is using NOMA technique, we first need to justify the problem. Simply put, NOMA can be divided into two key subproblems: channel assignment and power allocation. While serveral works have proposed to tackle these problems, there exists an approach of the optimization of power allocation known as joint resource allocation (JRA) method[[1]].
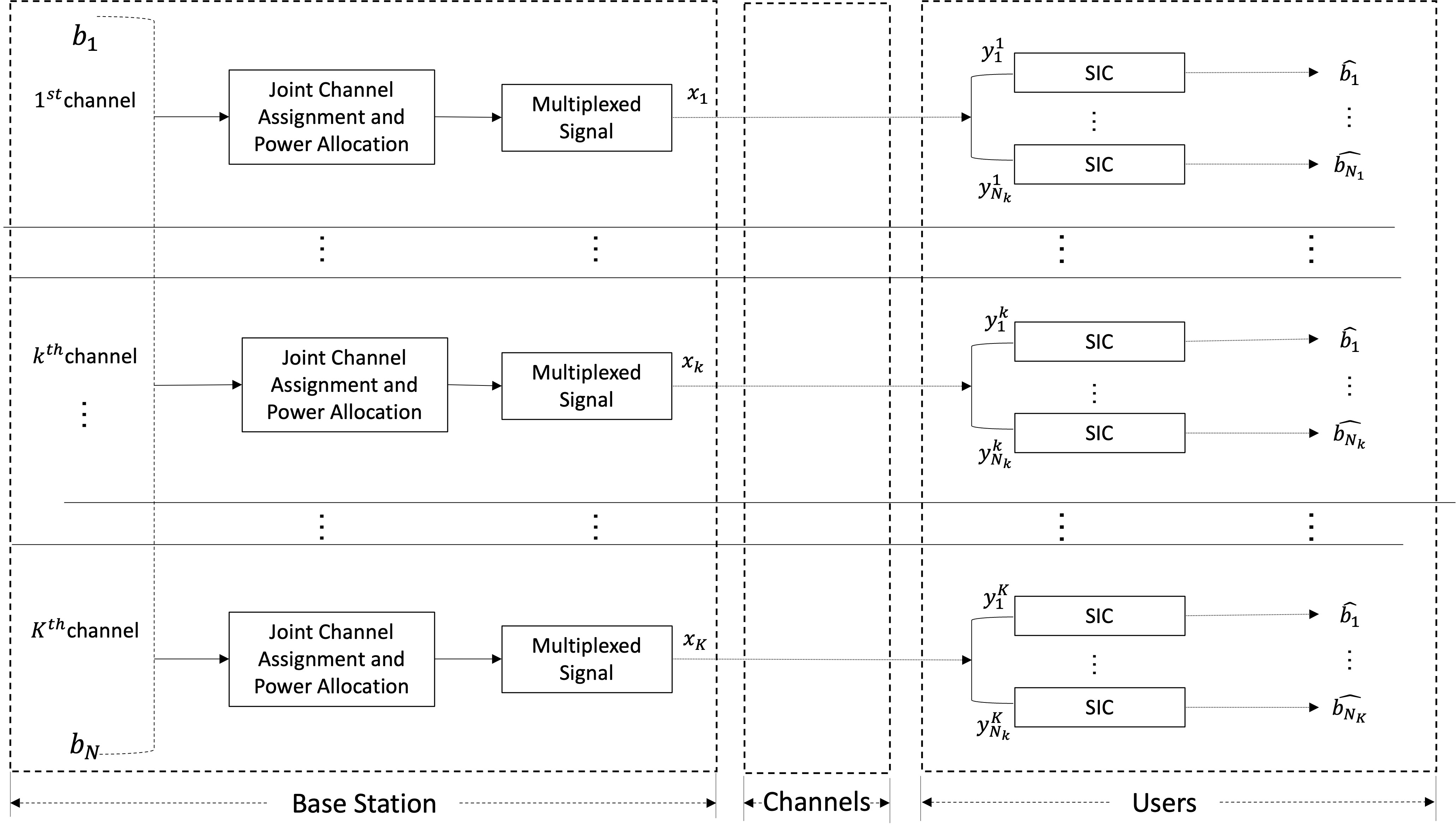
Figure 1. Transmission of BS and reception of users of the downlink NOMA system
Reference
[1] C. He, Y. Hu, Y. Chen and B. Zeng, “Joint Power Allocation and Channel Assignment for NOMA With Deep Reinforcement Learning,” in IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 37, no. 10, pp. 2200-2210, Oct. 2019, doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2933762.
References
2019
- Joint Power Allocation and Channel Assignment for NOMA With Deep Reinforcement LearningIEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019